Table of Contents
How Could Accenture’s Relationship to Extended Reality Be Described?

Hello users, here we are going tell you about How could Accenture’s relationship to extended reality be described and How Does The Image Relate To The Query – Accenture’s relationship to augmented reality (XR) can remain exploratory and innovative. The company invests heavily in XR research and development and works with clients to create new and innovative XR experiences.
Accenture’s XR Practice Helps Clients To:
- Imagine: Accenture helps clients to envision how XR can be used to transform their businesses.
- Create: Accenture develops custom XR solutions for clients, including VR training simulations, AR product demos, and MR collaboration tools.
- Deliver: Accenture helps clients to deploy and manage their XR solutions at scale.
- Accenture is also a leading provider of XR services, including XR consulting, XR design, and XR development.
How Does The Image Relate To The Query?
The image is a simple text overlay asking, “How could Accenture’s relationship to extended reality be described?” The image provides no additional information but reinforces that Accenture’s relationship to XR is still evolving.
The image is also relevant to the query because it remained on various web pages, including a page about Discord, a page about RBT competency, a page about Voltron Force, and a page about PowerPoint presentations. This suggests that Accenture’s XR work is relevant to various industries and applications.
What Is The Concept of Extended Reality?
Extended Reality (XR) remains an umbrella term that encompasses various technologies that merge the physical and digital worlds, providing immersive and interactive experiences that go beyond traditional virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). XR encompasses a spectrum of technologies, including:
Virtual Reality (VR): Creates a wholly immersive and simulated environment where users can interact with digital objects and surroundings using specialized headsets and controllers.
Augmented Reality (AR): Overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing the physical environment with interactive information and graphics.
Mixed Reality (MR): Blends the physical and digital worlds seamlessly, allowing users to interact with both simultaneously.
XR Technologies Offers a Range Of Benefits, Including:
- Immersive experiences: XR can transport users to virtual worlds or enhance the real world with digital elements, creating engaging and interactive experiences.
- Enhanced learning: XR can provide interactive and personalized learning experiences, making education more attractive and practical.
- Remote collaboration: XR enables virtual meetings and collaboration, breaking geographical barriers and facilitating teamwork.
- Training and simulation: XR can create realistic training simulations for various industries, such as healthcare, manufacturing, and aviation.
- Entertainment and gaming: XR offers immersive and interactive entertainment experiences, pushing the boundaries of storytelling and gaming.
- Design and prototyping: XR can visualize and prototype products, environments, and processes before physical creation.
- Healthcare and medical applications: XR can assist in surgical planning, patient education, and rehabilitation.
XR is still in the early stages of development, but it can potentially revolutionize various industries and aspects of our lives. As XR technologies mature and become more affordable, we can expect many real-world applications to emerge, transforming how we learn, work, play, and interact with the world around us.
What Is The Meaning Of Extended Reality XR?
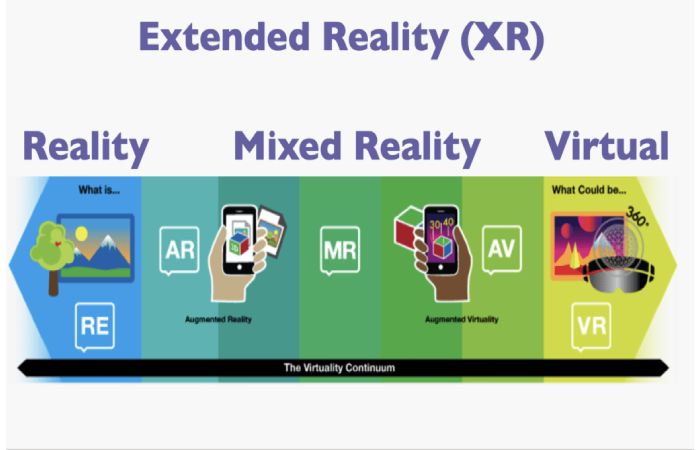
Extended Reality (XR) remains a broad term that encompasses various technologies that blend the physical and digital worlds to create immersive and communicative experiences. It goes beyond traditional virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to provide a more comprehensive and integrated experience.
Key Components of XR:
Virtual Reality (VR): VR creates an entirely immersive and simulated environment where users can interact with digital objects and surroundings using specialized headsets and controllers. VR transports users to virtual worlds, allowing them to explore and interact with virtual environments as if they were physically present.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, enhancing the physical environment with interactive information and graphics. AR blends the digital and physical worlds, providing users additional information and context about their surroundings.
Mixed Reality (MR): MR seamlessly blends the bodily and digital worlds, letting users interact with both simultaneously. MR creates a more immersive and interactive experience than AR, as users can manipulate and interact with digital objects in the real world.
Applications of XR:
- XR technologies can potentially revolutionize various industries and aspects of our lives. Here are some examples of potential applications:
- Education and Training: XR can provide interactive and personalized learning experiences, making teaching more engaging and effective. Immersive simulations and virtual environments can enhance learning outcomes and provide hands-on training experiences.
- Healthcare and Medical Applications: XR can assist in surgical planning, patient education, and rehabilitation. VR simulations can help surgeons visualize complex procedures and practice surgical techniques, while AR overlays can guide medical professionals during procedures.
- Design and Prototyping: XR can visualize and prototype products, environments, and processes before physical creation. Architects and creators can use VR to create 3D models of buildings and interiors, while engineers can use AR to overlay digital components onto physical prototypes.
- Entertainment and Gaming: XR offers immersive and interactive entertainment experiences, pushing the boundaries of storytelling and gaming. VR can transport players to virtual worlds and scenarios, while AR can enhance gaming experiences with interactive overlays and augmented gameplay.
- Remote Collaboration and Communication: XR enables virtual meetings and collaboration, breaking down geographical barriers and facilitating teamwork. Teams can collaborate on virtual projects, work on shared virtual whiteboards, and interact with virtual objects.
Retail and Shopping: XR can transform the shopping experience, allowing customers to try on clothes, explore virtual stores, and realistically interact with products. AR can overlay product information and reviews onto physical products, while VR can provide immersive virtual shopping experiences.
Future of XR:
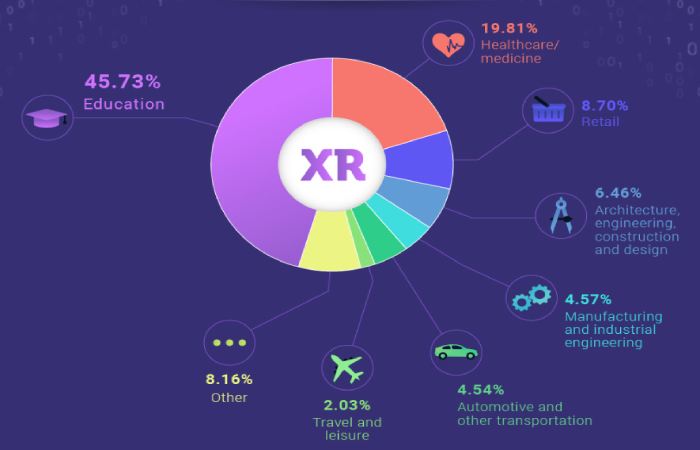
XR is still in its early stages of development, but its potential is immense. As XR technologies mature and become more affordable, we can expect many real-world applications to emerge, transforming how we learn, work, play, and interact with the world around us. XR has the potential to blur the lines between the bodily and digital worlds, creating new and exciting possibilities for the future.
Conclusion
Extended Reality (XR) remains a rapidly evolving field encompassing various technologies that blend the physical and digital worlds to create immersive and interactive knowledge. XR goes beyond traditional virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) to provide a more comprehensive and integrated experience, offering a range of benefits and applications across various industries.
